
中国农业科学院2日宣布,中国水稻研究所种质创新课题组研究发现了一个控制水稻籽粒锰积累的主效数量性状位点(QTL),并由此创制了高锰低镉水稻的优良育种材料,使高锰低镉水稻不再是育种家的梦想。相关研究成果新近在线发表于《科学报告》上。
该课题组首席专家钱前研究员介绍,锰作为一种重要的矿物质微量元素,在人类日常饮食中往往摄入不足;而水稻籽粒的锰含量虽然可以通过生物强化作用增加,但有害重金属镉含量也同时上升。这成为水稻育种领域一大难题,迄今未见有高锰低镉籽粒水稻种质材料的报道。
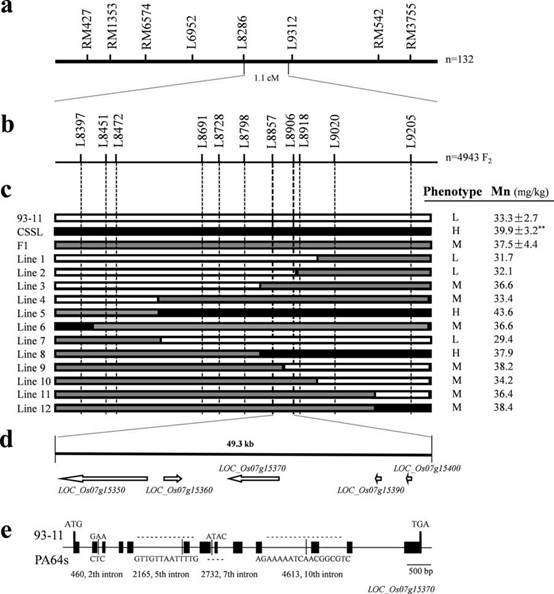
课题组研究人员利用低锰籼稻品种93-11和高锰品种培矮64s为亲本的重组自交系,结合高密度遗传图谱,在水稻第7号染色体短臂上检测到一个代号为qGMN7.1的控制籽粒锰含量的主效数量性状位点。qGMN7.1中包含一个调控锰镉吸收的基因(OsNRAMP5),启动基因表达的序列变异引起了转录水平的表达差异,导致籽粒锰浓度的变化。该研究表明,OsNRAMP5基因在调控水稻籽粒锰含量方面起了重要作用。以93-11为背景的qGMN7.1染色体片段代换系,其籽粒锰浓度显著上升,镉浓度显著下降,根系的锰吸收能力增强。
该项研究得到国家自然科学基金的资助。中国水稻研究所刘朝雷博士研究生为文章第一作者,钱前研究员和高振宇研究员为共同通讯作者。(来源:科技日报 瞿剑)
Characterization of a major QTL for manganese accumulation in rice grain
Abstract Some diets lack sufficient manganese (Mn), an essential mineral. Increasing Mn in grain by biofortification could prevent Mn deficiency, but may increase levels of the toxic element cadmium (Cd). Here, we investigated Mn in rice (Oryza sativa) grains in recombinant inbred lines (RILs) from the cross of 93–11 (low grain Mn) with PA64s (high grain Mn). Quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis to identify loci controlling grain Mn identified a major QTL, qGMN7.1, on the short arm of chromosome 7; qGMN7.1 explained 15.6% and 22.8% of the phenotypic variation in the RIL populations grown in two distinct environments. We validated the QTL with a chromosome segment substitution line (CSSL), CSSL-qGMN7.1, in the 93–11 background harboring qGMN7.1 from PA64s. Compared to 93–11, CSSL-qGMN7.1 grain had increased Mn and decreased Cd concentrations; CSSL-qGMN7.1 roots also showed enhanced Mn uptake. Fine mapping delimited qGMN7.1 to a 49.3-kb region containing OsNRAMP5, a gene responsible for Mn and Cd uptake. Sequence variations in the OsNRAMP5 promoter caused changes in its transcript level, and in grain Mn levels. Our study thus cloned a major QTL for grain Mn concentration in rice, and identified materials for breeding rice for high Mn and low Cd concentrations in the grain.
原文链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-18090-7.pdf



